What Is Gene therapy?
Contents
A processer, where a dysfunctional (bad gene) is replaced by a functional gene (good gene), this technique is called gene therapy.
Genes contain our DNA (it contains all the information necessary to build and maintain a body), if genes don’t work properly can cause diseases.
One of the most often used techniques is – Recombinant DNA technology, where a healthy gene is inserted into a vector, which can be plasmodial, nanostructured, or viral.
It is believed that gene therapy can treat a variety of diseases, such as cystic fibrosis, heart disease, thalassemia, hemophilia, AIDS, diabetes, and cancer.
NOTE: A vector (a carrier of disease or medication).
In today’s time, Feb/2022 – researchers are still studying gene therapy, like how to make it better in other birth-born diseases, and many more things.
NOTE: Not all medical fields that introduce alterations to a patient’s genetic makeup cannot be considered gene therapy.
In general, Bone marrow transplantation and Organ transplants, have been found to introduce foreign DNA into patients (1).
Types
Gene therapy has two main types, depending on which type of cells is in use.
Somatic cells
In a human, all the cells other than egg and sperm cells, are called somatic cells.
If we replace, this gene in any somatic cell, like blood, liver, or in a particular tissue, and cell, that type is called somatic gene therapy.
Mostly somatic gene therapy is approved. Remember, whatever process will happen with somatic cells, will not pass from the person to the next generation.
Somatic gene therapy represents mainstream basic and clinical research, In which therapeutic DNA is used to treat disease (4).
Germline cells
In this, only eggs and sperm cells are called germline cells.
I introduce, this gene in an egg or sperm cell then is called germline gene therapy. In germ cell, it could get a pass into the next generation.
It is not practiced much, due to the risk factors, like higher risks versus SCGT, due to ethnic issues, issues to future generations, etc.
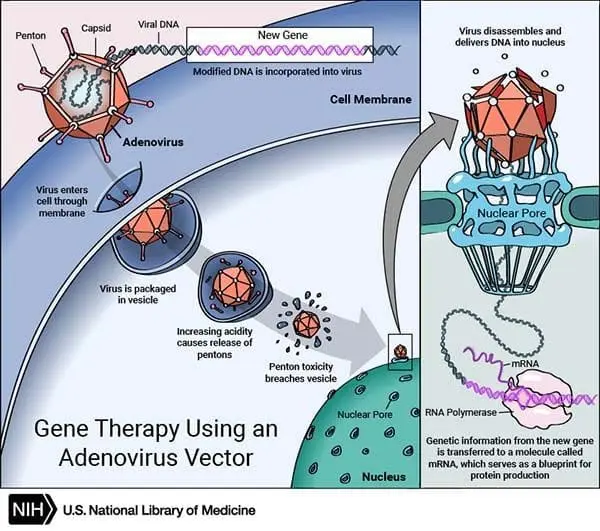
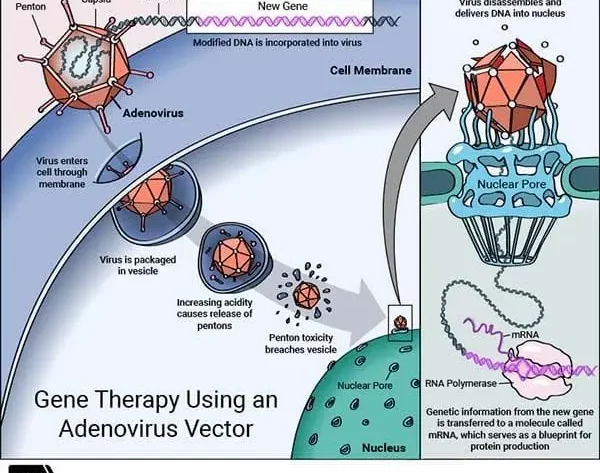
How Is it Work?
Gene therapy was first tried on a young girl in 1990 by French Anderson.
In this, a healthy gene is inserted into the genome (containing all genetic data of the body) to replace the abnormal gene, which is responsible for causing a certain disease.
But it has many challenges involved such as:
- Releasing genes into stem cells is difficulty
- lack of persistent gene ex- precision in targeted cells
- Immune responses to viral gene
Once the vector (Which is used to release the gene) Is inserted into the patient, it is considered successful treatment only in some conditions. include:
- It cannot induce an allergic reaction or any inflammatory process
- It should work as a normal function
- It should be safe for patients, and also for the environment.
- The vector should be capable to express the gene for the patient’s entire life (2) (3).
NOTE: The doctor can do gene therapy in 2 ways – Ex-vivo and In-vivo gene therapy.
You can understand its working process through the images given above.
What Is Ex-Vivo and In-vivo gene therapy?
Ex-vivo – In this, tissue is removed from the body, it could be bone marrow cells, which are taken out to grow, then a functional gene introduced in them, where they grow.
And when the specialist will get the correct base, then they will introduce that gene into the patient’s body, which is called Ex-vivo gene therapy.
The whole process happens outside the body. Ex vivo gene therapies are better tolerated and have less risk of severe immune responses.
In-vivo – In this, directly introducing the gene into the patient body is called in-vivo gene therapy.
In 2021, Both In vivo and ex-vivo therapeutics are seen as safe.
NOTE: For this work, specialists need vectors to introduce the genes into the body (6).
Vectors
There are mainly 2 types of vectors used – gone viral, and the second a non-viral vector.
Viral vector
It is also known as a viruses vector, In this, these virus is mainly used include:
- Retrovirus – Because it can integrate into the host cells.
- Adenoviruses – Because it has good property, which can make counterpart DNA from RNA.
- Herpes simplex virus – is also known as human alpha herpes virus 1 and 2.
Viruses also have some disadvantages such as – may interact with other body parts, triggering the immune system, etc.
Non-viral vector
Non-viral vectors present certain benefits compared to viral vectors, such as – large-scale production and low host immunogenicity.
There are several non-viral vectors methods including – Pure DNA, Human artificial chromosome, bone marrow cells, oligonucleotides, lipoplexes, etc.
Non-viral techniques may offer repeat dosing and greater tailorability (capable of being adapted to a given purpose) of genetic payloads, and the future will be more based on this.
Method
There are both physical and chemical are available.
Physical methods
Gene gun – In this, a high-frequency shot is given so that this gene complex is directly going into the tissue.
Microinjection – In this micropipette is used to introduce this particular gene.
Chemical methods
Detergent mixture – In this, a normal gene introduces by mixing it with a chemical compound.
Lipofection – A lipid compound (a chemical that is insoluble in water and soluble in alcohol, ether, and chloroform) is used to introduce normal genes in the body.
Pros
It has many advantages (pros ) including:
- It can help reverse many mutations.
- Can prevent hereditary disorders (a disease that passes from generation to generation) like thalassemia, type 1 diabetes, etc.
Cons
Some of the unsolved problems or disadvantages include:
- Its current result is not long-lasting.
- Gene therapy is not yet available for all disorders.
- It brings with it a lot of immunity risks for example – specialists cannot control a gene if it goes in the wrong direction so it can bring some diseases.
- Viral vector – It can bring with it inflammation, infection, toxicity, gene control, and targeting issues.
- Multigene disorder – Some are – heart disease, High BP, Alzheimer’s disease, arthritis, and diabetes are affected by multiple genes.
- Some therapies may break the “Weismann barrier protecting” the testes, potentially modifying the germline.
- Cost – Its recent cost is very high, It was reported in 2013, to be the world’s most expensive drug.
What Does Research Say?
Gene therapy was first tried on a young girl in 1990 by French Anderson. The effects were successful but temporary (8).
In 2003, a research team inserted genes into the brain for the first time, and they used viral vectors, that were small enough to cross the blood-brain barrier.
In October 2003, in China, Medicine became the world’s first gene therapy approved for commercial production (9).
In March 2006, researchers announced the successful use of gene therapy in two adult patients with a genetic disorder, that affects myeloid cells and damages the immune system.
In May 2007, researchers announced the first gene therapy trial for inherited eye disease.
Many research was done from 2007 to 2021 in which some were successful and some were not.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved only a limited amount of gene therapy products for sale in the United States.
There are hundreds of research still pending, on gene therapy as a treatment of genetic conditions such as cancer, and HIV/AIDA.
NOTE: There is still a lot of research still pending on gene therapy.
BOTTOM LINE
Not all medical fields that introduce alterations to a patient’s genetic makeup cannot be considered gene therapy.
In gene therapy, a healthy gene is inserted into the genome to replace the abnormal gene, which is responsible for causing a certain disease.