What Is Dopamine?
Contents
Dopamine is a type of hormone made in the brain, responsible for the feeling of happiness, which works as a neurotransmitter.
First – Our hormones are responsible for every emotion we have like in a stressful situation body releases the cortisol hormone.
What is a neurotransmitter? – Our brain is made up of special cells called neurons or nerve cells.
Our nervous system uses it to send messages between nerve cells through electrochemical signals, which are sometimes called chemical messengers.
It is also responsible for the Pleasure and Reward feelings, which is why is also known as the pleasure neurotransmitter.
NOTE: When we are happy dopamine is released. Due to this we feel good and feel like doing that work again and again. Which include:
- While eating food
- During sex
- Shopping
- music
- Traveling
- And anything else, that makes us happy
NOTE: keep this happiness, or satisfaction in control, Otherwise, getting dopamine for any work will become a bad habit of yours.

What Do They Do In Our Bodies?
Dopamine (DOP) play varieties of role in the body, which production of which makes us feel happy, satisfied, and when we receive a reward.
This pleasure or feeling good comes from several things that become a habit by repeatedly stimulating the release of dopamine.
Apart from happiness or satisfaction feeling, dopamine also plays a vital role in both physical and behavioral functions including:
- Learning
- Increase heart rate
- High blood pressure
- Motivated person to work hard
- Gives you a warm fuzzy feeling of pride and reward, when you complete everything you wanted to do.
- control nausea and vomiting
- Sleep
- Mood
- pain processing
But triggering too much or too low (DOP) can lead to various health issues such as Parkinson’s disease.
Parkinson’s disease or a disorder, where the central nervous system is affected, caused by dopamine neuron deficiency.
NOTE: There are some drugs, alcohol, and food like coffee and candy that make the body produce more dopamine.
What exactly has the dopamine come from?
It all starts with the food that we eat, for example, when we eat bananas one of the nutrients that we consumed is tyrosine (an amino acid).
Which is absorbed into the body, and then goes to the brain, where an enzyme called tyrosine hydroxylase, runs a series of events in tyrosine, which convert tyrosine into dopamine.
But how does our brain know when to release dopamine?
There is a system in our brain called the reward system, which is found in both animals and humans.
This system is designed to reward you when you’re doing things that advance your survival this includes eating, sexual, and kissing.
By doing this thing, the brain knows it is a good thing, instead of which the brain released a bunch of good chemicals and a reward system, called dopamine.
What Happen If Body Produce Too much dopamine?
If the body produces too much dopamine, whether it is outer or inner reasons, which makes you feel out of the world. but temporarily.
But too much also has some side effects which include:
Effect on mental health
- Addiction
- Being more competitive
- Aggressive
- Loss of motor control and ability to normal movement leads to tremors and fatigue.
- hallucination
NOTE: If the addiction to get dopamine is a bad thing like alcohol, illegal drugs, etc. then it can ruin the body.
Effect on body
- obesity
- poor mental and physical health
- change in appetite causes weight loss
- Addiction withdrawal may lead to headache, anxiety, depression, difficulty in sleeping, etc
- organs failure
- Even death, of addiction, is very high.
It is believed that the reason for getting addicted to anything is the pleasure received after the release of dopamine in high quantity.
That’s why humans repeatedly use that thing from which they get pleasure and later it becomes an addiction.
How Drugs Affect Dopamine?
When It is released, a person would want to do it again and again whenever they feel hungry.
Drugs of abuse hack the system, turning the person’s natural needs into drug needs.
Imaging studies have shown that drug abusers have seen decreases in dopamine D2 receptors and dopamine release.
Most drugs of abuse increase dopamine, in the reward pathway, and some common drugs such as alcohol, heroin, and nicotine.
Which indirectly triggers DOP production at a high level, and causes a fast, or more intense dopamine rush, compared to a cup of dark coffee.
Medicine that increases dopamine activity could be an effective treatment for alcohol abuse disorders, conflicting results have been produced (3).
Once a habit is formed, the mind forces you to take that particular substance, by which the same peace and pleasure feeling gets again (4).
Different drugs hit dopamine in different ways, but the general result is that dopamine is produced in the synapse in greater amounts than usual.
This causes continuous overstimulation of receiving neurons and is responsible for long and fast excitement experienced by drugs users.
What is a Synapse? – There is a small gap between the end of one neuron and the beginning of another neuron called a synapse.
Continuous intake of drugs eventually desensitizes the reward system, which leads the system to no longer respond to everyday stimuli.
Even after some time, drugs lose their ability to reward and higher doses are required to feel the same happiness, this leads to a drug overdose.
Trigger dopamine again and again for a long time lose interest in many things, and it also becomes very difficult to give up.
What If Body Produces Too Low Dopamine?
If the body produces too low dopamine, which makes the person less motivated and excited, caused by various mental disorders, some like:
- Depression
- Hallucinations
- Parkinson’s disease
Other things may also cause low dopamine production, such as – a diet high in sugar and fats can suppress dopamine,
A study showed that obese people are more prone to low deficiency of dopamine.
Some common effects are also seen in both mental and physical health which include:
- Weight loss or weight gain
- Lack of sleep
- Muscle cramps
- Pains
- Loss of balance
- Feel low energy
- Sad feeling
- lack of focus and concentration
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease
- Feel demotivated
- Constipation
- Mood swings
- low self-esteem and confidence
- low libido
- Depression, weird thoughts
- Feel guilty
Dopamine Structure Diagram
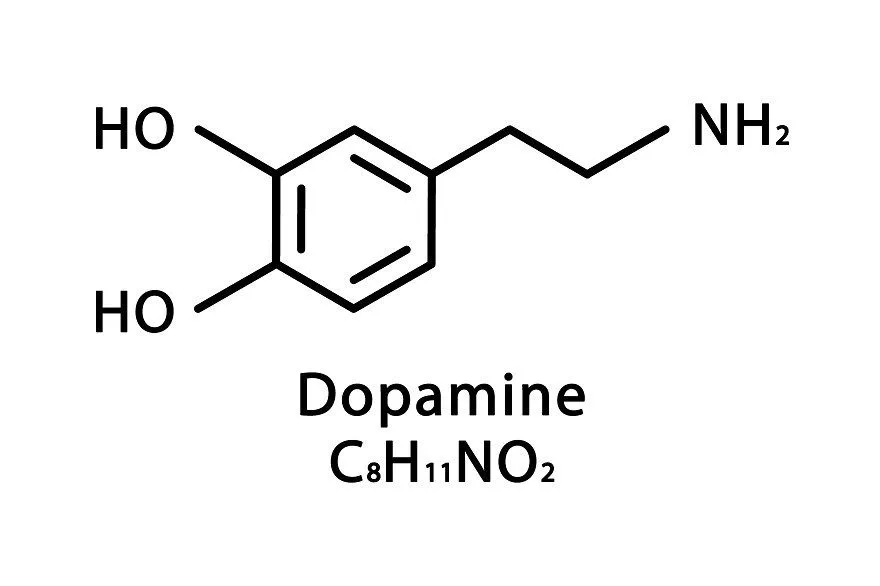
Dopamine is an organic base, As a base, it is generally protonated in acidic environments (is an acid-base reaction)
The protonated form is highly water-soluble and relatively stable but can oxidize if it contacts oxygen or other oxidants (5).
Medical Uses
It is also manufactured in form of medicines that are sold by trade names like Intropin, Dopastat, etc (6).
It is used to treat low blood pressure, low heart rate, and cardiac arrest, especially given in newborn infants, through intravenous drip instead of injection (7).
Dopamine has a very short half-life in plasma, it is about 1 minute in adults, 2 minutes in a newborn, and 5 minutes in premature infants.
Even high and low doses of it can cause different effects in the body which include:
- High doses can lead to increased muscle contraction, heart rate, urination output, blood pressure, and increased cardiac output.
- Low doses can also cause narrow blood vessels, which lead to increases in blood pressure (8).
However, a study review showed that very low doses may be harmful including kidney function issues, and irregular heartbeat (9).
BOTTOM LINE
Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that plays several roles in the brain, and also affects physical health.
It is one of those chemicals that is responsible for transmitting signals b/w the nerve cells in the brain these cells are called neurons.
Talk to your doctor, if you have noticed lower or high BP, Fast heartbeat, and any other discomfort, because it may be a sign of an underlying medical condition.
With Consistent use, the drugs lose the ability to reward, and higher doses are required to feel the same happiness, which leads to a drug overdose.



